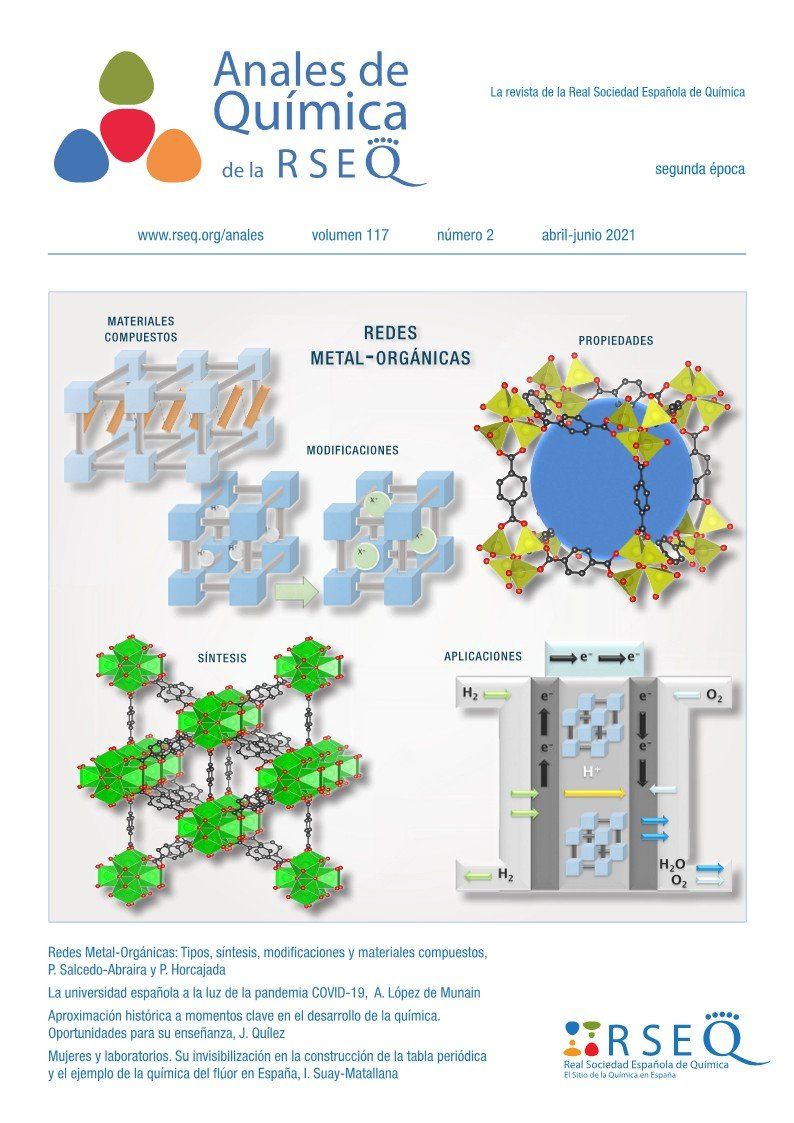
Abstract
Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) are a type of crystalline porous solid, built up from polydentate linkers and inorganic centers, with important potential applications (e.g., separation, catalysis or biomedicine, among others). This review describes the huge chemical and structural versatility of these multifunctional materials, referring to type-examples. In addition, the generally used synthetic methods are described, together with the different strategies applied to enhance their properties via their compositional modification (e.g., functionalization, composite materials).

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Copyright (c) 2021 Pablo Salcedo Fernández, Patricia Horcajada Cortés